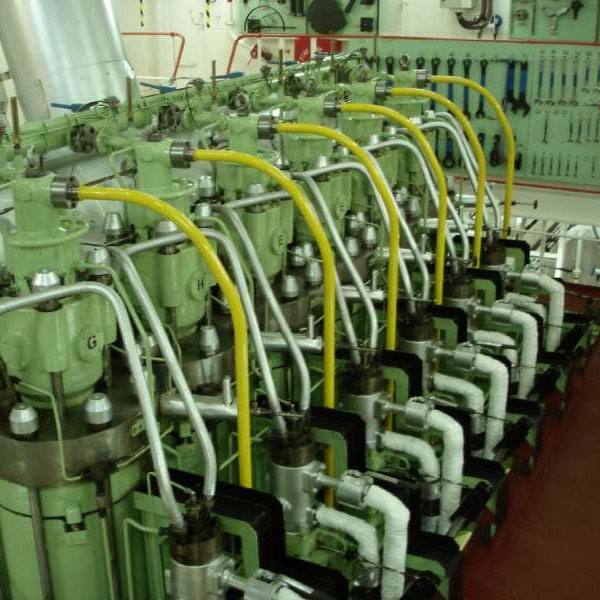
Overhaul Main Engine/ DC/Aux Machinery
Terms and conditions Applied
Overhaul Main Engine/ DC/Aux Machinery
The overhaul of the Main Engine, Direct Current (DC) systems, and Auxiliary Machinery plays a critical role in ensuring the efficient operation and longevity of marine vessels and industrial machines. Routine maintenance and timely overhauls help prevent unexpected breakdowns, reduce operational costs, and ensure optimal performance. In this article, we will provide an in-depth guide to overhauling these essential components of machinery.
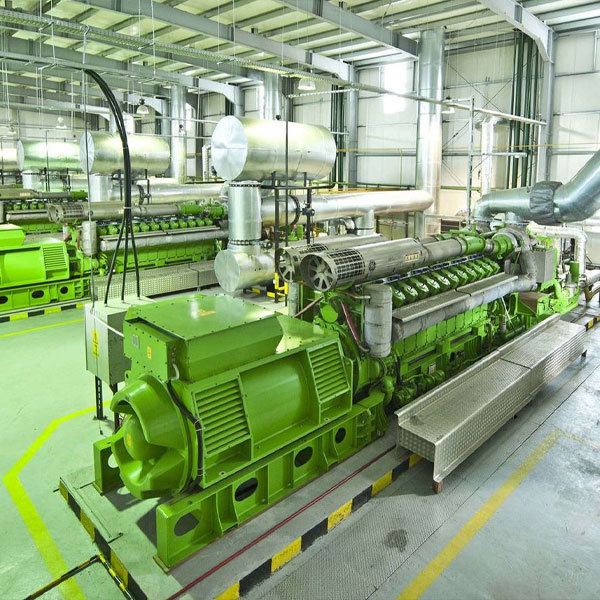
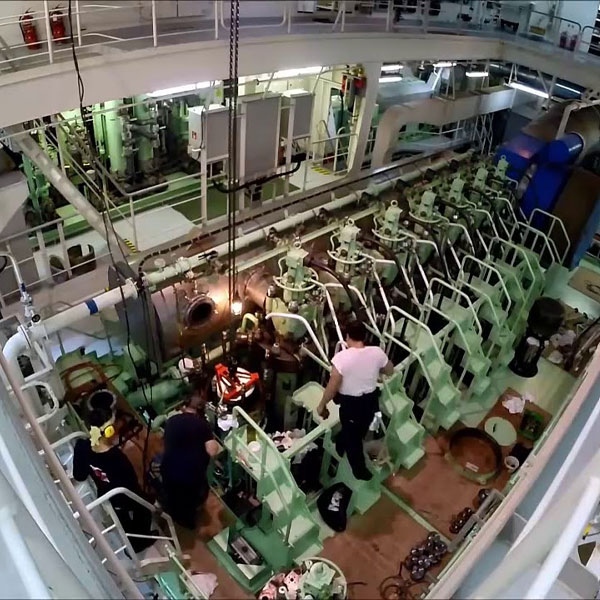

Understanding the Importance of an Overhaul
The main engine, along with DC and auxiliary machinery, forms the heart of any industrial or marine operation. These systems undergo tremendous strain during normal operations. Overhauling refers to a detailed inspection, cleaning, and refurbishment process that is conducted periodically to maintain machine performance.
The benefits of overhauling these systems include:
- Increased efficiency: Regular overhauls ensure components are operating at their full potential.
- Extended lifespan: By replacing worn-out parts, the overall life of the machinery is significantly prolonged.
- Safety improvements: A thorough overhaul reduces the risk of malfunctions, leading to safer working conditions.
Importance of Documentation
Documenting the overhaul process is a crucial aspect often overlooked. Comprehensive records of the procedures carried out, including parts replaced, inspections made, and test results, provide a valuable reference for future maintenance and troubleshooting. Keeping track of all past overhauls ensures that any trends in wear or malfunction are identified early, thus preventing potential failures.
Step-by-Step Process of Overhauling the Main Engine
Preparation for Main Engine Overhaul
Before commencing the overhaul, it is essential to prepare adequately:
- Ensure Shutdown of the Engine: The engine must be cooled down and properly shut off before beginning the overhaul process.
- Secure Safety Equipment: Workers should use protective gear such as gloves, helmets, and eye protection, and follow all safety protocols.
- Inspect and Record Initial Conditions: Documenting the current condition of the engine is critical for later comparisons. Take note of unusual noises, vibrations, or leaks.
Dismantling of Main Engine Components
Once the preparation phase is complete, the dismantling process begins:
- Cylinder Head Removal: The cylinder head is removed first to access internal components such as pistons and liners.
- Piston and Connecting Rod Removal: The piston, connecting rod, and crankshaft are carefully dismantled, ensuring that all parts are numbered and marked for easy reassembly.
- Crankcase Inspection: The crankcase should be thoroughly inspected for wear and tear, especially checking for signs of metal fatigue or oil deposits.
Cleaning and Inspection
After dismantling, each component undergoes a detailed cleaning and inspection:
- Cleaning: Parts like pistons, cylinder heads, and liners should be cleaned using specialized solvents to remove carbon deposits and other contaminants.
- Inspection: Each part is visually inspected and measured for signs of wear. Key areas to inspect include:
- Piston Rings: Look for signs of wear or cracking.
- Liners: Check for scoring or cracks.
- Bearings: Ensure there is no excessive wear or misalignment.
- Crankshaft: Inspect the journals and fillets for any signs of distortion or fatigue.
Replacement and Refurbishment of Worn Parts
Based on the inspection, worn-out parts are either replaced or refurbished. Commonly replaced parts include gaskets, bearings, and piston rings. Some components, such as the crankshaft or connecting rods, may require specialized machining to restore them to operational standards.
Reassembly of the Main Engine
After cleaning and replacing worn components, the engine is reassembled:
- Piston and Cylinder Head Installation: The pistons and cylinder heads are carefully reinstalled. Proper alignment and torque specifications must be followed to avoid future issues.
- Lubrication System Check: Ensure that the engine’s lubrication system is functioning properly to prevent wear during operation.
Post-Overhaul Testing
Once reassembly is complete, the engine is started for post-overhaul testing:
- Initial Run: Start the engine at low RPMs and gradually increase to ensure smooth operation. Monitor for any unusual sounds or vibrations.
- Temperature and Pressure Monitoring: Ensure that oil and coolant temperatures and pressures remain within operational limits.
Types of Marine Surveys
There are several types of marine inspection surveys that are regularly conducted to ensure vessels remain compliant and operational:
Pre-Purchase Surveys
These are typically conducted when a vessel is being bought or sold. The surveyor assesses the condition of the ship, helping the buyer make an informed decision about the purchase.
Condition Surveys
These are conducted periodically to determine the current state of a vessel’s structure and equipment. They help identify potential risks and areas that require maintenance or repairs.
Damage Surveys
When a vessel experiences damage due to an accident or harsh environmental conditions, a damage survey is conducted to assess the extent of the damage and recommend repairs.
On-Hire/Off-Hire Surveys
These are performed when a vessel is being rented or returned to ensure that it is in suitable condition and to document any damages that occurred during the hire period.
Safety Surveys
Safety surveys focus on the vessel’s lifesaving and fire-fighting equipment, as well as other safety protocols, ensuring that all safety-related systems comply with international standards.
Understanding Marine Audits
Marine audits are another critical aspect of maritime safety and compliance. Unlike surveys, which focus on the physical condition of the vessel, audits assess the operational procedures, safety management systems, and compliance with industry standards and best practices.
Overhauling DC Machinery
DC machinery, which includes components such as generators and motors, also requires regular overhauls. The steps for overhauling DC machinery are similar to that of the main engine but with specific focus on electrical components.
Inspection of Electrical Components
- Brushes and Commutators: DC systems rely on brushes and commutators to maintain electrical contact. These components should be inspected for wear, pitting, and burning.
- Insulation Check: Inspect the windings for signs of insulation breakdown or overheating.
Cleaning and Replacing Worn Parts
Electrical components are cleaned using appropriate solvents to remove dirt and debris that may hinder performance. Worn brushes and commutators are replaced to ensure continued efficient operation.
Testing and Calibration
After the overhaul, the DC machinery must undergo testing to ensure proper operation. This includes:
- Electrical Testing: Verify the voltage, current, and resistance to ensure optimal electrical performance.
- Load Testing: Run the machinery under load to check for proper operation and stability under working conditions.
Auxiliary Machinery Overhaul Process
Auxiliary machinery refers to the various support systems that aid the operation of the main engine, such as pumps, air compressors, cooling systems, and hydraulic systems. Overhauling auxiliary machinery follows a similar pattern to main engine and DC systems.
Inspection and Dismantling
Auxiliary equipment is first inspected for leaks, unusual noises, and signs of wear. The equipment is then dismantled, and key components such as bearings, seals, and valves are inspected.
Cleaning and Replacement of Parts
After dismantling, parts are thoroughly cleaned and any worn or damaged components are replaced. Seals and gaskets, in particular, are prone to wear and should be replaced during every overhaul.
Reassembly and Testing
Once all parts are cleaned and worn components replaced, the auxiliary equipment is reassembled. Testing ensures that pumps and compressors are operating within their specified pressure and temperature ranges.
Conclusion
Regular overhauls of the main engine, DC, and auxiliary machinery are essential for ensuring reliability, safety, and efficiency in industrial and marine operations. By following a structured overhaul process that includes thorough inspections, cleaning, replacement of worn components, and rigorous testing, you can ensure these critical systems remain in peak operating condition.

